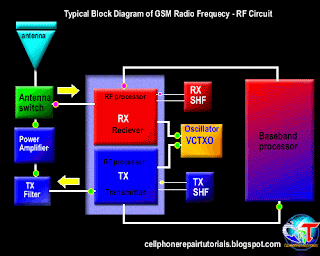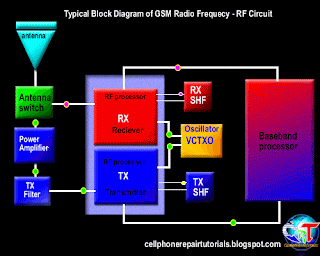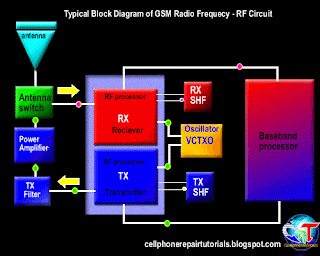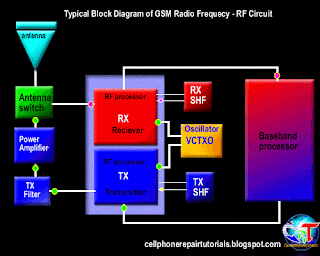
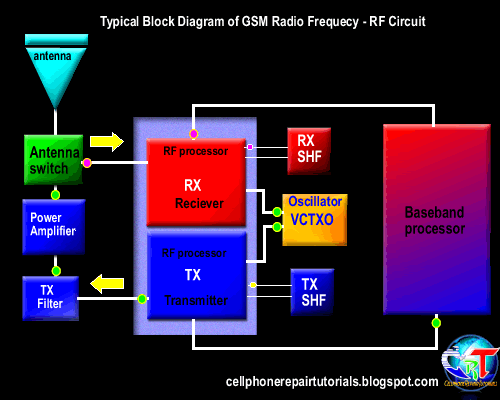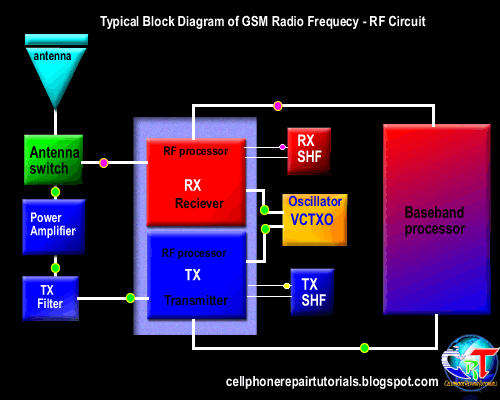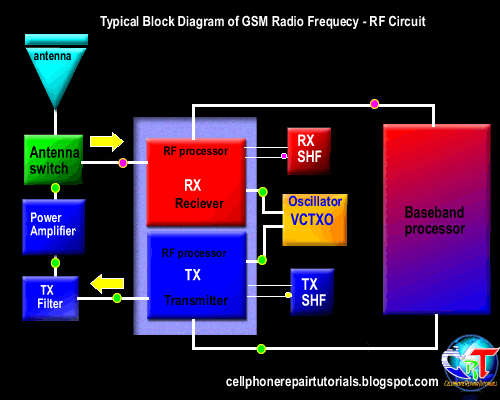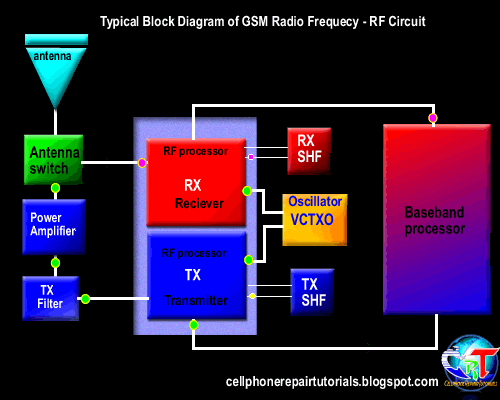
Definition of Abbreviations on Mobile Phones Circuit
0
2G 2nd Generation
3G 3rd Generation
3Gs 3rd Generation speed
4G 4th Generation
A
A/D-converter Analog-to-digital converter
ACI Accessory Control Interface
ADC Analog-to-digital converter
ADSP Application DPS (expected to run high level tasks)
AGC Automatic gain control (maintains volume)
ALS Ambient light sensor
AMSL After Market Service Leader
ARM Advanced RISC Machines
ARPU Average revenue per user (per month or per year)
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
ASIP Application Specific Interface Protector
B
B2B Board to board, connector between PWB and UI board
BB Baseband
BC02 Bluetooth module made by CSR
BIQUAD Bi-quadratic ,type of filter function)
BSI Battery Size Indicator
BT Bluetooth
C
CBus MCU controlled serial bus connected to UPP_WD2,UEME and Zocus
CCP Compact Camera Port
CDSP Cellular DSP (expected to run at low levels)
CLDC Connected limited device configuration
CMOS Complimentary metal-oxide semiconductor circuit (low power consumption)
COF Chip on Foil
COG Chip on Glass
CPU Central Processing Unit
CSR cambridge silicon radio
CSTN Color Super Twisted Nematic
CTSI Clock Timing Sleep and interrupt block of Tiku
CW Continuous wave
D
D/A-converter Digital-to-analouge converter
DAC Digital-to-analouge converter
DBI Digital Battery Interface
DBus DSP controlled serial bus connected between UPP_WD2 and Helgo
DCT-4 Digital Core Technology
DMA Direct memory access
DP Data Package
DPLL Digital Phase Locked Loop
DSP Digital Signal Processor
DtoS Differential to Single ended
E
EDGE Enhanced data rates for global/GSM evaluation
EGSM Extended GSM
EM Energy management
EMC Electromagnetic compability
EMI Electromagnetic interference
ESD Electrostatic discharge
F
FCI Functional cover interface
FPS Flash Programming Tool
FR Full rate
FSTN Film compensated super twisted nematic
G
GND Ground, conductive mass
GPIB General-purpose interface bus
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GSM Group Special Mobile/Global System for Mobile communication
H
HF Hands free
HFCM Handsfree Common
HS Handset
HSCSD High speed circuit switched data (data transmission connection faster than GSM)
HW Hardware
I
I/O Input/Output
IBAT Battery current
IC Integrated circuit
ICHAR Charger current
IF Interface
IHF Integrated hands free
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity
IR Infrared
IrDA Infrared Data Associasion
ISA Intelligent software architecture
J
JPEG/JPG Joint Photographic Experts Group
L
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LDO Low Drop Out
LED Light-emitting diode
LPRF Low Power Radio Frequency
0
2G 2nd Generation
3G 3rd Generation
3Gs 3rd Generation speed
4G 4th Generation
A
A/D-converter Analog-to-digital converter
ACI Accessory Control Interface
ADC Analog-to-digital converter
ADSP Application DPS (expected to run high level tasks)
AGC Automatic gain control (maintains volume)
ALS Ambient light sensor
AMSL After Market Service Leader
ARM Advanced RISC Machines
ARPU Average revenue per user (per month or per year)
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
ASIP Application Specific Interface Protector
B
B2B Board to board, connector between PWB and UI board
BB Baseband
BC02 Bluetooth module made by CSR
BIQUAD Bi-quadratic ,type of filter function)
BSI Battery Size Indicator
BT Bluetooth
C
CBus MCU controlled serial bus connected to UPP_WD2,UEME and Zocus
CCP Compact Camera Port
CDSP Cellular DSP (expected to run at low levels)
CLDC Connected limited device configuration
CMOS Complimentary metal-oxide semiconductor circuit (low power consumption)
COF Chip on Foil
COG Chip on Glass
CPU Central Processing Unit
CSR cambridge silicon radio
CSTN Color Super Twisted Nematic
CTSI Clock Timing Sleep and interrupt block of Tiku
CW Continuous wave
D
D/A-converter Digital-to-analouge converter
DAC Digital-to-analouge converter
DBI Digital Battery Interface
DBus DSP controlled serial bus connected between UPP_WD2 and Helgo
DCT-4 Digital Core Technology
DMA Direct memory access
DP Data Package
DPLL Digital Phase Locked Loop
DSP Digital Signal Processor
DtoS Differential to Single ended
E
EDGE Enhanced data rates for global/GSM evaluation
EGSM Extended GSM
EM Energy management
EMC Electromagnetic compability
EMI Electromagnetic interference
ESD Electrostatic discharge
F
FCI Functional cover interface
FPS Flash Programming Tool
FR Full rate
FSTN Film compensated super twisted nematic
G
GND Ground, conductive mass
GPIB General-purpose interface bus
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GSM Group Special Mobile/Global System for Mobile communication
H
HF Hands free
HFCM Handsfree Common
HS Handset
HSCSD High speed circuit switched data (data transmission connection faster than GSM)
HW Hardware
I
I/O Input/Output
IBAT Battery current
IC Integrated circuit
ICHAR Charger current
IF Interface
IHF Integrated hands free
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity
IR Infrared
IrDA Infrared Data Associasion
ISA Intelligent software architecture
J
JPEG/JPG Joint Photographic Experts Group
L
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LDO Low Drop Out
LED Light-emitting diode
LPRF Low Power Radio Frequency
MCU Micro Controller Unit (microprocessor)
MCU Multiport control unit
MIC, mic Microphone
MIDP Mobile Information Device Profile
MIN Mobile identification number
MIPS Million instructions per second
MMC Multimedia card
MMS Multimedia messaging service
N
NTC Negative temperature coefficient, temperature sensitive resistor used as a
temperature sensor
O
OMA Object management architechture
OMAP Operations, maintenance, and administartion part
Opamp Operational Amplifier
P
PA Power amplifier
PDA Pocket Data Application
PDA Personal digital assistant
PDRAM Program/Data RAM (on chip in Tiku)
Phoenix Software tool of DCT4.x
PIM Personal Information Management
PLL Phase locked loop
PM (Phone) Permanent memory
PUP General Purpose IO (PIO), USARTS and Pulse Width Modulators
PURX Power-up reset
PWB Printed Wiring Board
PWM Pulse width modulation
R
RC-filter Resistance-Capacitance filter
RF Radio Frequency
RF PopPort TM Reduced function PopPortTM interface
RFBUS Serial control Bus For RF
RSK Right Soft Key
RS-MMC Reduced size Multi Media Card
RSSI Receiving signal strength indicator
RST Reset Switch
RTC Real Time Clock (provides date and time)
RX Radio Receiver
S
SARAM Single Access RAM
SAW filter Surface Acoustic Wave filter
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory
SID Security ID
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
SMPS Switched Mode Power Supply
SNR Signal-to-noice ratio
SPR Standard Product requirements
SRAM Static random access memory
STI Serial Trace Interface
SW Software
SWIM Subscriber/Wallet Identification Module
T
TCXO Temperature controlled Oscillator
Tiku Finnish for Chip, Successor of the UPP, Official Tiku3G
TX Radio Transmitter
U
UART Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter
UEME Universal Energy Management chip (Enhanced version)
UEMEK See UEME
UI User Interface
UPP Universal Phone Processor
UPP_WD2Communicator version of DCT4 system ASIC
USB Universal Serial Bus
V
VBAT Battery voltage
VCHAR Charger voltage
VCO Voltage controlled oscillator
VCTCXO Voltage Controlled Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator
VCXO Voltage Controlled Crystal Oscillator
Vp-p Peak-to-peak voltage
VSIM SIM voltage
W
WAP Wireless application protocol
WD Watchdog
X
XHTML Extensible hypertext markup language
Z
Zocus Current sensor, (used to monitor the current flow to and from the battery)